GStreamer application development guide
1. Introduction
1.1. terminologies
¡ element
- filter element
- S/W module
- pipeline의 구성요소
¡ bin
- a set of element
- sub pipeline
¡ pipeline
- a set of element
- element들 혹은 bin 형태의 element를 지닐 수 있음
¡ bus
- pipeline은 기본적으로 bus를 지님
- pipeline의 bus를 get 하고 여기에 callback을 등록하면, 메시지를 받을 수 있음
- u EOS 등의 stream message 등을 application에서 받을 수 있음
¡ Pads and capabilities
. +-----------+ +-------------+
| +-----+ +------+ |
| src | src | ---- | sink | sink |
| +-----+ +------+ |
+-----------+ +-------------+
pad link
¡ gst_element_link_pads (source, "src", demux, "sink");
¡ Request pad
- . element는 request pad들을 지님
- . 자동으로 생성되는 pad는 아니고 on demand에서 생성됨
- . teeing 시 혹은 multiplexing/aggregation 시 유용
1.2. Advanced GStreamer concepts
. application-pipeline interaction using dynamic parameters and interfaces
. threading and threaded pipelines
. scheduling and clocks (and synchronization)
1.3. Higher-level interfraces for GStreamer applications
. autopluggers
. playbin
- ¡ playbin
- ¡ uridecodebin
- ¡ decodebin
2. automatic detection of pipieline
¡ autoplugging
: high-quality autopluggers
¡ typefinding
¡ capabilities as a way for elements
: 이전 chapter에서 다룬 내용
¡ Media stream type detection
first need to detect the stream type
Typefinding
During this period, it will provide data to all plugins
that implement a typefinder
stream의 recognization 시 signal 발생
¡ how to use the typefind element
gst_bin_add_many (GST_BIN (pipeline), srcelem, typefind, fakesink, NULL);
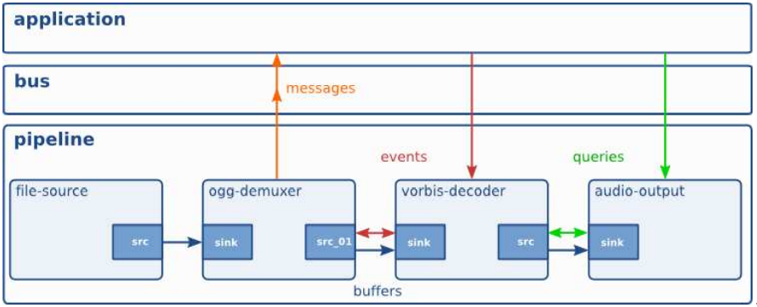
2.1. Communication
¡ buffers
- source -> sink
¡ events
- app에서 보내던가, element간 보냄
- event 방향
- u upstream
- u downstream
- data flow에 sync.
¡ messages
- element가 pipeline의 message bus에 post함
¡ queries
- app이 duration등의 정보를 요청
3. Initializing GStreamer
4. Elements
5. Bins
5.1. bins manages states of their children
¡ bin에서 gst_element_set_state
- 모든 contained element들에 대해 상태 천이 유도
- bin은 sink element부터 source까지 상태 천이를 수행함
¡ 동작중인 pipeline에 elem 추가 시,
- pad-added signal callback 내에서 state는 자동으로 변경되지 않음
- target의 state를 설정해야 함
gst_element_set_state
gst_elemt_sync_state_with_parent
6. Bus
¡ message 전달
streaming threads --> app 으로의 message 전달
¡ bus
모든 pipeline은 bus가 있음
app에서는 message를 처리할 message handler를 준비해야 함
¡ message handler는
- GObject의 signal handler와 비슷함
- mainloop에서 주기적으로 message를 check하고 처리
¡ main loop check callback등록
- gst_bus_add_watch
- gst_bus_add_signal_watch
를 통해 message를 main loop에서 check 할 수 있음
6.1. Message typs
¡ pre-defined message types
- error
- EOS
- tags
stream에서 찾은 metadata를 emit함
- state-changes
- buffering
network-stream의 caching 중에 발생
- element messages
특정 element에 속하는 특별한 message들 임
- application-specific messages
7. Pads and capabilities
¡ pad의 properties
2개 존재
source와 sink pad
¡ dynamic pads
pad의 생성이 element의 생성때 함께 이뤄지지 않는 pad임
Ogg의 경우 Ogg strearm을 읽고 난 후 dynamic pad를 생성함
이런 경우, gst-inspect를 oggdemux를 돌리면,
한개의 sink pad만 있다고 나옴
다른 pad는 dormant
exists: Sometimes property
¡ dynamic pipeline의 생성 시 반드시 고려해야 함
signal handler를 attach하여
element가 새로운 pad의 생성 시 알림을 받을 수 있음
새로운 pad는 sometimes pad template에서 생성됨)
cb_new_pad(...) {
...
name = gst_pad_get_name (pad);
g_free (name);
/* here, you would setup a new pad link for the newly created pad */
....
}
demux = gst_element_factory_make ("oggdemux", "demuxer");
/* listen for newly created pads */
g_signal_connect (demux, "pad-added", G_CALLBACK (cb_new_pad), NULL);
이런 식으로 pad를 생성하는 경우는 흔한 경우가 아님
이 경우 반드시 newly-added elem에 대해 pipeline의 state(즉, target state)로
elem의 state를 manually set 해야 함 (gst_element_set_state)
7.1.1. Request pads
7.2. Capabilities of a pad
A pad’s capabilities are described in a GstCaps
¡ negotiated pad
: capability set을 지님
¡ unnegotiated pad 혹은 pad template은
: 지닐 수도 있고 아닐 수도 있음
¡ gst-inspect vorbisdec
Pad Templates:
SRC template: ’src’
Availability: Always
Capabilities:
audio/x-raw
format: F32LE
rate: [ 1, 2147483647 ]
channels: [ 1, 256 ]
SINK template: ’sink’
Availability: Always
Capabilities:
audio/x-vorbis
properties로 capabilities의 info를 기술
property는 key/value pair임
7.3. What capabilities are used for
¡ Capabilities (short: caps)
data의 type을 기술함
이는,다음에 사용됨
Autoplugging
Compatibility detection
2개 pad의 link 시 verify를 위함
Metadata
pad의 capability에 대한 meta data read
Filtering
app에서 capability의 제약 시 사용
“filtered caps”를 통해
video size의 제약 등을 수행할 수 있음
7.3.1. Using capabilities for metadata
GstCaps는 GstStructure의 array로 여러 set을 표현
example of how to extract the width and height from a set of fixed video caps
read_video_props (GstCaps *caps) {
GstStructure *str = gst_caps_get_structure (caps, 0);
gst_structure_get_int (str, "width", &width);
...
}
7.3.2. Creating capabilities for filtering
¡ data type forcing
filtered cap을 사용하고자 하는 경우, 이를 통해 type의 제약을 하고자 할때,
GstCaps를 만들고,
GstCaps *caps = caps = gst_caps_new_simple ("video/x-raw",
"format", G_TYPE_STRING, "I420",
"width", G_TYPE_INT, 384,
"height", G_TYPE_INT, 288,
"framerate", GST_TYPE_FRACTION, 25, 1,
NULL);
link_ok = gst_element_link_filtered (element1, element2, caps);
이렇게 하면 2 elem간 data type을 forcing 할 수 있음
더 상세한 cap 제약도 가능함
7.4. Ghost pads
pad가 없는 bin
이 경우 ghost pads가 필요
¡ ghost pad
bin에서의 어떤 elem의 pad임
bin으로부터 바로 access 가능한 pad 임
(UNIX system의 symbolic link 개념과 유사)
ghost pad를 사용하는 bin은 특정 pad를
다른 곳에서 transparently 사용할 수 있도록 사용
+-----------------------------------------------+
+------+ +---------------+ +----------+ |
| sink |----| elem 1 | | elem 2 | |
+------+ +------+ +-----+ +------+ | |
| | sink | | src |--->| sink | | |
| +------+ +-----+ +------+---+ |
| |
+-----------------------------------------------+
¡ caps negotiation
GstCaps
buffer와 event가 pad간 흐름
버퍼는 GstBuffer이고 이는 reference를 전달하기에 버퍼링에대한 오버헤드는 기본적으로는 없음
- u 앱이 주는것 이벤트와 쿼리
- u 앱이 받는것 메시지
파이프라인 혹은 빈에 이미 add된 element에 대해서만 link가 가능함
다른 계층에 있는것을 link 하려면 ghost pad를 사용해야함
고스트 패드는 bin 내의 앞단 elem의 sink가 고스트 패드로서 사용됨
해당 elem의 pad로 bin의 ghost pad로 지정
elem은 bin에 added
¡ element states
NULL 리소스 할당 없음
READY 리소스는 할당 단 stream pointer는 zero
PAUSED 버퍼링을 수행 디코더등은 아무일 안함
PLAYING clock이 동작함만 paused와 차이
¡ state 전파
상태는 pipeline 혹은 bin에 적용 시 하위 elements에 보다 propagate
sink 부터 source 순서
sink의 pause로의 상태변화는 src에 flushing error를 야기하여 src가 paused 상태로 변하기 전에 재생이 실질적으로 멈추게됨 (streaming thread를 멈춤)
동작중인 pipeline에 elem 추가 시 pad added signal callback 등에서 state를 원하는 상태로 변경해야함
¡ bin
- a container element
¡ query
- 위치 query와 duration query
- st_element_query_position () and gst_element_query_duration
- query는 싱크부터 올라가면서 처리 가능 elem까지 전달됨
8. Position tracking and seeking
9. meta data
¡ stream tag
- 작곡가명, 곡명 등
- GStreamer tagging dydtem으로 획득
- GST_MESSAGE_TAG msg에서 획득
- 여러번 올라오기에 모아서 잘 보여줘야함
- gst_tag_list_merge가 보통 사용됨
- e GST_TAG_MERGE_PREPEND
¡ strream info
- size, resolution, codec name
- pad의 caps로 획득
12.2. Tag writing
테그를 파일에도 쓸 수 있음
10. Interfaces
interface는 elem 획득 시 사용
¡ uri의 형태
- file:///…
- http://...
- mms://…
g filename to uri
g uri to filename등의 함수 사용으로 커버팅 가능
gst element make from uri
소스나 싱크 타입에대해 elem 획득 가능 함수
¡ color balance interface
는 여러 plugin들로 구현됨
xvimagesink
Video4Linux element등 포함
¡ Playback tutorial 5: Color Balance
https://gstreamer.freedesktop.org/documentation/tutorials/playback/color-balance.html
Brightness, Contrast, Hue and Saturation
¡ video overlay interface
위 2개 외 ximagesink sdlsink등으로 구현됨
window handle을 넘기면 거기에 비디오를 그림
11. Clocks and synchronization in
¡ Non-live sources
file에서 읽고
동기화된 방식으로 재생
여러 stream들이 동기화 되어야 함 (audio/video/subtitle)
¡ capture
여러 live source에서의 media를 muxing/mixing
오디오와 비디오의 녹화 (from microphone/camera)
¡ streaming (from slow network) with buffering
보통 web streaming case이며, 이는 http를 통해 streaming server에 접근
network
web streaming (from http server)
¡ capture from live source & playback to live source with configurable latency
카메라 녹화 중 효과 적용
UDP로부터의 low latency streaming
¡ simultaneous live cpature + playback from prerecorded content
이전 녹음된 것을 재생하면서 레코딩 하는 경우
이전에 녹음된 것과 완벽히 동기화 된 녹음을 하기 위함
¡ GstClock object
buffer timestamps
¡ SEGMENT event
11.1. Clock running-time
clock time은 늘 0부터 시작하지는 않음
last reboot 시점에서의 lcock, known start date 등을 사용
¡ GstClock
gst_clock_get_time에 따른 absolute-time을 리턴
monotonically increasing (순증가)
이 절대 시간을 가지고 running-time이 계산됨
base-time이라고 불리우는 이전 snapshot때의 absolute-time
runnig-time = absolute-time - base-time
¡ clock time
순증가 (절대 시간) - system clock time임
¡ running time
재생이 진행되는 시간
전체 재생 이후 replay 되는 시간까지 순증가
0부터 증가
¡ stream time
media duration 중 positon을 의미
0부터 증가
¡ base time
재생이 시작되는 시점의 clock time임
재생은,
clock-time - base-time = running-time
위 수식이 동일한 경우 buffer는 재생 됨
¡ GstPipeline 객체
playing state에서
GstClock 객체와 base-time을 유지
pipeline은 선택된 GstClock에 대한 handle을 각 elem에 줌
with selected base-time
¡ pipeline 내 모든 객체들은
동일 clock과 base-time을 지님
즉, 모든 elem은 running-time을 계산 할 수 있음
11.2. Buffer running-time
¡ buffer running-time 계산
buffer가 제공하는
buffer timestamp와 SEGMENT event가 필요
¡ gst_segment_to_running_time()
SEGMENT event를 GstSegment 객체로 전환
이후
gst_segment_to_running_time()로 buffer running-time을 계산
¡ sync
보통 sink elem에서 수행
sink는 pipeline에 설정된 latency를 고려하고 이것을
buffer running-time에 더한 후 pipeline clock에 동기화 함
¡ Non-live sources
의 timestamp buffers는 0부터 시작
flushing seek 이후 buffer는 다시 runnig-time이 0부터
¡ live sources
buffer의 최초 byte가 capture 되었을 때의
pipeline running-time에 matching하는 running-time 사용
11.3. Buffer stream-time
¡ stream-time이 stream 내 position임
buffer timestamps와 이전 SEGMENT event를 가지고 계산됨
¡ media 내의 time을 표현
0에서 total duration 사이의 시간
¡ used for
POSITION query 시 현재 시간 report
seek event에서 사용되는 position
controlled value에 대한 동기화에 사용되는 position
¡ stream-time은
stream의 sync에는 사용되지 않음
sync는 running-time으로만 수행됨
11.4. Clock providers
¡ pipielien 내 GstClock을 제공하는 elem임
재생 rate는 system clock rate에 맞추는 것이 아님
보통 audio에 맞춤
ex. 44.1 KHz
internal clock을 지닌 elem이 동기화 필요 시,
언제 pipeline clock에 대한 시간이 내부 clock에 따라 발생하는지를 추정해야 함
추정하려면, 이것의 clock을 pipeline clock에 종속 시켜야 함
pipeline clock이 정확히 elem의 internal clock과 같다면,
elem은 종속 과정이 필요 없고
직접 pipeline clock을 써서 playback의 schedule을 하면 됨
(이것이 더 빠르고 정확함)
그래서 보통 audio input과 같은 혹은 output device과 같은 internal clock을 지닌 elem은,
pipeline에 대한 clock provider가 됨
pipeline이 PLAYING state가 되면,
이것은 sink 부터 source까지 pipeline 내 모든 elem에 대해 전파되며,
elem에게 clock을 제공할 수 있는지 물어봄
¡ clock을 제공할 수 있는 last elem이 clock provider로 사용됨
보통의 playback pipeline에서는 audio sink가 선호됨
capture 시에는 source element에서의 clock이 사용됨
¡ bus message
clock과 clock provider를 알리는 bus message가 있음
NEW_CLOCK message on the bus
clock provider가 pipeline에서 제고되면, CLOCK_LOST message가 발생함
app은 이 경우 PAUSED 상태로 가야 하고 새로운 clock을 선택해야 함
11.5. Latency
¡ latency
timestamp X에서 capture된 sample이 sink까지 도달하는데 걸리는 시간
이 시간은 pipeline 내 clock에 반대되어 측정됨
clock에 반대되어 동기화 되는 elem들은 sink들 뿐임
buffer를 지연 시키는 elem이 없기에 latency는 늘 0임
live source의 pipeline 경우,
latency가 존재
live source에서 존재
¡ audio source 경우,
최초 sample은 time 0에서 capture됨
source가 buffer를 44100 sample들을 push 하면, at 44100 Hz
1초의 버퍼임
buffer의 TS는 0이고 clock의 시간이 now >= 1 sec. 이기에
sink는 이 buffer를 drop함 (늦었기에)
sink에서 latency compensation이 없다면, 모든 buffer는 drop됨
11.5.1. Latency compensation
¡ LATENCY query
모든 sink에 대해 수행됨 (in pipeline)
pipeline은 maximum latency를 선택하고 이것을 LATENCY event로 설정
LATENCY event에 의해 모든 sink elem은 재생을 지연
모든 sink은 동일 시간의 지연을 지니기에, 모두 sync에 상대적임
11.5.1.1. Dynamic Latency
pipeline에 elem의 add/remove 시, 혹은 elem의 prop 수정 시, latency가 변경 될 수 있음
elem은 pipeline 내 latency의 change에 대해 LTENCY message를 bus로 보내 알림
app은 이것을 받고 새로운 latency를 재분배할지 말지 결정해야 함
pipeline 내 latency의 변경은 들을수있는 혹은 볼 수 있는 glitch를 유발
그렇기에 app에 의해서만 수행 되어야 함
12. Buffering
+---------+ +---------+ +-------+
| httpsrc | | buffer | | demux |
| src - sink src - sink ....
+---------+ +---------+ +-------+slow network에서 read 후 buffer라는 queue에 저장
¡ buffer element는
low, high watermark를 지님 (단위는 bytes)
¡ watermark 사용 방식
아래 1~4 내용 (demuxer가 push mode 인 경우에만 해당)
BUFFERING message에서
high watermark인 경우 -> 재생 상태 진입
low watermark인 경우 -> pause하여 buffering 상태 진입
1) buffer Element의 BUFFERING message
buffer element는 high watermark에 도달 할 때까지 BUFFERING message를 post
이를통해 app은 pipeline의 PAUSED를 유지하는 시점을 알 수 있음
이는 sink에서 data가 preroll되는 동안 srcpad가 pushing하는 것을 pause함
2) high watermark에 도달하면,
BUFFERING message는 100%를 알리며 post 됨 -> app은 이때 playback continue 하면 됨
3) 재생 중, low watermark에 도달 시 (hit),
queue는 BUFFERING message를 다시 보냄
이로서 app은 high watermark까지pipeline을 다시 PAUSE 시킴 <- rebuffering stage
4) 재생 중 queue level은 high와 low 사이를 fluctuate 할 수 있음
network irregularities를 compensate하기 위해서
이 buffering method는
demuxer가 push mode로 동작 시 사용 가능
seek은 network source에 대해서 수행 됨
효과적인 seeking이 안되된가 live streaming 처럼 총 량을 알 수 없는 경우, 사용이 바람직함
¡ wateramrk 설정
low와 high에 대한 good value를 설정해야 함
watermark 설정 시 고려 점
1) network bandwidth
이후 watermark 설정 - buffering이 fixed amount time 소모 시
queue2 element가 지닌 property
max-size-time property
use-rate-estimate property
playbin이 지닌 property
buffer-duration
: rate estimate으로 buffering 할 data의 size를 결정
2) codec bitrate
재생 전에 얼마만큼의 고정량의 data가 필요한지 판단하는데 사용
buffering element는 stream의 bitrate를 알 수 없으나 query 하여 획득 가능
3) 고정 amount of bytes로 시작
rebuffering의 시간을 측정
app에서 limit으로 설정한 rebuffering 시간 동안 queue의 size를 증가
¡ buffering element
pipeline 어디든 삽입 가능
예를들어
u decoder element 앞에 삽입 가능
u 이를 통해 low/high watermark설정 가능
¡ playbin의 buffering flag
buffering은 parsed data에 대해 수행
later state에 대해 buffering 하는 것의 장점은,
demuxer가 pull mode로 동작하게 할 수 있다는 것
12.1. Download buffering
+---------+ +---------+ +-------+
| httpsrc | | buffer | | demux |
| src - sink src - sink ....
+---------+ +----|----+ +-------+
V
file
server에서 고정 크기의 file을 streaming 시,
app은 전체 file을 disk로 download 여부를 결정 할 수 있음
이 때, buffer element는
push와 pull 기반의 srcpad를 demuxer로 제공하여
downloaded file을 navigate할 수 있게 함
* client가 총 량을 알 수 있는 경우만 적합함
이 경우,
요구되는 range가 downloaded area + buffersize 내에 없을 시, buffering message가 발생
buffering message는 incremental download가 수행중이라는 걸 알리는 indication 포함
-> app이 buffering을 보다 지능적으로 수행 가능하게 해 줌
(using the BUFFERING query - see 15.5)
12.2. Timeshift buffering
+---------+ +---------+ +-------+
| httpsrc | | buffer | | demux |
| src - sink src - sink ....
+---------+ +----|----+ +-------+
V
fie-ringbuffer
이 mode에서, 고정 크기의 ring buffer가 download된걸 유지
ring buffer의 size에 의존해 buffered data에 대해서는 seeking 가능
12.3. Live buffering
live pipeline에서,
capture와 playback element 간 fixed latency가 존재
발생원인
1) queue에 의해 발생 (such as a jitterbuffer)
2) audiosink에서의 buffering 등
이런 live pipeline에 대해서도 BUFFERING message는 발생 가능
이를 통해 latency buffering에 대해 user가 알 수 있게 함
app은 보통 이런 state changed를 지닌 buffering message에 대응하지 않음
12.4. Buffering strategies
buffering message와 buffering query를 기반으로 여러 다른 buffering 전략의 구현 방법에 대한 idea
1) No-rebuffer strategy
pipeline으로 충분한 data를 buffering 하여 끊김없는 재생 가능
이를 위해서는 file의
남은 총 재생 시간
남은 총 download 시간
을 알아야 함
if buffering time < playback time
즉, 재생 보다 buffering이 빠르면,
이 경우 방해없이 재생 가능
위의 정보들을 획득하려면, 다음의 query들을 사용하여 가능
DURATION
POSITION
BUFFERING
이 query들을 주기적으로 수행해서 buffering status를 파악할 수 있음
전체 file을 hold하기 위한 충분히 큰 buffer가 필요함
15.2에서 확인 가능한 download strategy가 바로 이것
#include <gst/gst.h>
GstState target_state;
static gboolean is_live;
static gboolean is_buffering;
static gboolean
buffer_timeout (gpointer data) {
GstElement *pipeline = data;
GstQuery *query;
gboolean busy;
gint percent;
gint64 estimated_total;
gint64 position, duration;
guint64 play_left;
query = gst_query_new_buffering (GST_FORMAT_TIME);
if (!gst_element_query (pipeline, query))
return TRUE;
gst_query_parse_buffering_percent (query, &busy, &percent);
gst_query_parse_buffering_range (query, NULL, NULL, NULL, &estimated_total);
if (estimated_total == -1)
estimated_total = 0;
/* calculate the remaining playback time */
if (!gst_element_query_position (pipeline, GST_FORMAT_TIME, &position))
position = -1;
if (!gst_element_query_duration (pipeline, GST_FORMAT_TIME, &duration))
duration = -1;
if (duration != -1 && position != -1)
play_left = GST_TIME_AS_MSECONDS (duration - position);
else
play_left = 0;
g_message ("play_left %" G_GUINT64_FORMAT", estimated_total %" G_GUINT64_FORMAT
", percent %d", play_left, estimated_total, percent);
/* we are buffering or the estimated download time is bigger than the
* remaining playback time. We keep buffering. */
is_buffering = (busy || estimated_total * 1.1 > play_left);
if (!is_buffering)
gst_element_set_state (pipeline, target_state);
return is_buffering;
}
static void
on_message_buffering (GstBus *bus, GstMessage *message, gpointer user_data) {
GstElement *pipeline = user_data;
gint percent;
/* no state management needed for live pipelines */
if (is_live)
return;
gst_message_parse_buffering (message, &percent);
if (percent < 100) {
/* buffering busy */
if (!is_buffering) {
is_buffering = TRUE;
if (target_state == GST_STATE_PLAYING) {
/* we were not buffering but PLAYING, PAUSE the pipeline. */
gst_element_set_state (pipeline, GST_STATE_PAUSED);
}
}
}
}
static void
on_message_async_done (GstBus *bus, GstMessage *message, gpointer user_data) {
GstElement *pipeline = user_data;
if (!is_buffering)
gst_element_set_state (pipeline, target_state);
else
g_timeout_add (500, buffer_timeout, pipeline);
}
gint
main (gint argc,
gchar *argv[]) {
GstElement *pipeline;
GMainLoop *loop;
GstBus *bus;
GstStateChangeReturn ret;
/* init GStreamer */
gst_init (&argc, &argv);
loop = g_main_loop_new (NULL, FALSE);
/* make sure we have a URI */
if (argc != 2) {
g_print ("Usage: %s <URI>\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
/* set up */
pipeline = gst_element_factory_make ("playbin", "pipeline");
g_object_set (G_OBJECT (pipeline), "uri", argv[1], NULL);
g_object_set (G_OBJECT (pipeline), "flags", 0x697 , NULL);
bus = gst_pipeline_get_bus (GST_PIPELINE (pipeline));
gst_bus_add_signal_watch (bus);
g_signal_connect (bus, "message::buffering",
(GCallback) on_message_buffering, pipeline);
g_signal_connect (bus, "message::async-done",
(GCallback) on_message_async_done, pipeline);
gst_object_unref (bus);
is_buffering = FALSE;
target_state = GST_STATE_PLAYING;
ret = gst_element_set_state (pipeline, GST_STATE_PAUSED);
switch (ret) {
case GST_STATE_CHANGE_SUCCESS:
is_live = FALSE;
break;
case GST_STATE_CHANGE_FAILURE:
g_warning ("failed to PAUSE");
return -1;
case GST_STATE_CHANGE_NO_PREROLL:
is_live = TRUE;
break;
default:
break;
}
/* now run */
g_main_loop_run (loop);
/* also clean up */
gst_element_set_state (pipeline, GST_STATE_NULL);
gst_object_unref (GST_OBJECT (pipeline));
g_main_loop_unref (loop);
return 0;
}
¡ pipeline의 PAUSED 상태 설정
buffering이 필요한 경우에 preroll state 에서는 buffering message를 받음
u on_message_async_done이 발생하는 경우가 prerolled state임
이 경우, buffering이 going on인지 여부를 확인 하여
그렇지 못한 경우 재생을 시작함
buffering이 going on 상태였다면, buffering state를 poll하기위해 timeout을 시작해야 함
download 예상 시간이 남은 재생 시간보다 작다면, playback을 시작하면 됨
13. Dynamic Controllable Parameters
13.1. Getting Started
¡ controller subsystem
stream-time에 대해 gobject properties를 설정하는 간단한 방법을 제공
보통은 g_object_set을 통해 property가 변경됨
u 이를 신뢰성 있는 timing에 처리하는 것은 거의 불가능함
¡ control-binding
control-sources를 properties에 붙이는 것으로서 이 controller는 time을 고려함
control-value를 gobject property에 map
u .type을 converting 하고 target property value range로 값을 scaling 함
run-time에서 element는 current stream-time이 gobject properties를 update할 수 있도록
u value의 변화를 계속 pull 함
gst는 몇 개의 control-source들과 control-binding들을 이미 포함하고 있음
(in the core library, gstcontroller library)
그러나 app은 각각의 base class들의 sub-classing을 통해 app 용으로 정의해야함
¡ 대부분의 controller mechanism은 GstObject로 구현됨
¡ Control-sources
- 주어진 time-stamp에 대한 value를 제공함 (보통 0.0~1.0 사이의 값)
¡ 사용방법
gstreamer-controller을 link하고, 다음과 같이 include
...
#include <gst/gst.h>
#include <gst/controller/gstinterpolationcontrolsource.h>
#include <gst/controller/gstdirectcontrolbinding.h>
...
linker에
pkg-config for gstreamer-controller-1.0
를 사용해서 필요한 것들을 모두 linker와 compiler를 위해 지정 가능
13.2. Setting up parameter control
pipeline에 대해 parameter 제어를 하고자 하면,
¡ 1) control-source 생성
ex. interpolation control-source 사용 경우
csource = gst_interpolation_control_source_new ();
g_object_set (csource, "mode", GST_INTERPOLATION_MODE_LINEAR, NULL);
¡ 2) control-binding 수행
control-source를 gobject property에 attach
하나의 control-source는 별도의 control-binding을 통해 여러 object property에 attach 가능함
gst_object_add_control_binding (object, gst_direct_control_binding_new (object, "pr
이런 type의 control-source는 time-stamped parameter의 변경에 대한 list로부터 새로운 property value를 취함
source smoothing parameter changes를 통해 gap을 채울 수 있음
이런 행동은 control-source의 mode property의 세팅을 통해 설정될 수 있음
다른 control source 중에는 sin() 함수의 호출을 통해 value들의 stream을 생성하는 것도 있음
이 source의 경우 주파수 설정 parameter등이 있음
control-source가 GstObjects이면, control-source들을 이런 properties에 역시 attach 가능함
몇몇 control point의 set이 가능하며,
time-stamped gdouble value들은 보통 0.0에서 1.0 사이의 값을 지님
1.0의 값은 target properties의 value range에 maximum value에 map 됨
timestamp에 도달하면 값은 active 됨
도달해도 값들은 여전히 list 내에 유지됨
만약 pipeline이 segmented seek을 사용해서 loop를 run 하고 있다면,
control-curve도 반복됨
GstTimedValueControlSource *tv_csource = (GstTimedValueControlSource *)csource;
gst_timed_value_control_source_set (tv_csource, 0 * GST_SECOND, 0.0);
gst_timed_value_control_source_set (tv_csource, 1 * GST_SECOND, 1.0);
이제 모든것이 play 준비 상태가 되었음
만약 control-source가 volume property에 bound 되면, 1초에 대해 fade-in으로 향하게 됨
한가지 주의할점은, gstreamer로 온 volume element의 volume propery 상에서는 value rage가 0.0에서 4.0임
이 경우, 위의 control-source가 volume property에 attach 되면, 400%까지 ramp up 됨
built-in live mode
property가 control-source를 지니고 있다고 해도
assigned one은 g_object_set을 통해 GOject property를 변경할 수 있음
GObject property를 GUI widget에 bindig 시켰을 경우에 매우 유용함
user가 Widget으로 값을 조절 시, one은 GObject property를 set 할 수 있고 다음 설정에 의해 값이 override될 때까지 유효함
smoothed parameter에 대해서도 마찬가지임
단, property를 끊임없이 update하는 control-source에 대해서는 동작하지 않음
(e.g. the lfo_control_source)
14. Threads
gstreamer는 multi-threaded 되어 있으며, thread-safe 함
대부분은 app에 노출되지 않음
단, 특정한 경우 application은 thread를 직접 운영해야 할 수도 있음
14.1. Scheduling in GStreamer
pipeline 내 각 element는 자신이 어떻게 schedule될지 결정할 수 있음
어떤 element가 sink pad로부터 pulling/혹은
source pad 상에서의 pushing을 위해 thread를 start하기 위해, thread를 운영할 수 있음
element는 또한 push 그리고 pull mode 각각을 위한 data processing을 위해
upstream 혹은 downstream thread를 사용할 수 있음
GST는 어떻게 schedule될지에 대해서는 제약을 두지 않음
see. "the Plugin Writer Guide" for more details
data processing을 위해 thread 사용 시 (streaming thread),
streaming thread는 (혹은 GstTask object는) GstTaskPool을 통해 생성됨
이제 tasks와 pools에서 어떻게 notification을 받는지 설명할 것임
14.2. Configuring Threads in GStreamer
¡ STREAM_STATUS
- bus message이며, streaming thread의 상태를 알려줌
- 이 message에서는 다음의 정보를 획득 할 수 있음
. new thread가 생성되려 할 때,
GST_STREAM_STATUS_TYPE_CREATE으로 해당 message를 수신
이후 GstTask 내에서 GstTaskPool 설정 가능
custom taskpool은 streaming threads의 구현을 위해 task를 위한 custom thread를 제공함
custom taskpool을 사용하고자 한다면, 동기화된 방식으로 해당 message는 다뤄져야 함
15. Autoplugging
automatically detect the media type of a stream and automatically generate the best possible pipeline
자동으로 최적의 elem을 찾아서 pipeline을 구성하고자 할 때 사용되는 기능
system에서 available한 elem을 찾아서 수행함
¡ high-quality autopluggers
¡ Media types
stream을 식별하는데 사용됨
media type에 대한 agreement는 negotiation 시 pad에 있는 capability의 media type으로 결정
elem은 반드시 src/sink 각각 pad에 media type과 연관
u GStreamer registry에 elem 별 type에 대해 저장 되어 있음

file-srouce의 src pad: any
ogg-demuxer의 sink pad: application/ogg
src pad: audio/x-vorbis
vorbis-decoder
sink pad: audio/x-vorbis
src pad: audio/x-raw, format=F32LE
converter
sink pad: audio/x-raw, format=F32LE
src pad: audio/x-raw, format=S16LE
audio-output
sink pad: audio/x-raw, format=S16LE
media type과 property들
보통 많이 사용되는 format에서는 stream에 대한 property 기술이 필요 없음
media type만 필요
media type과 property들에 대한 full list는 Pligin Writer's Guide에 명시
typefinding 과 autoplugging
¡ 1) media stream에서 type 찾기
¡ 2) type으로 pipeline 구성하기
15.1. Media stream type detection
media stream의 loading 시에는 type을 알 수 없는것이 보통임
pipeline 구성 전 stream type을 알아야 함
¡ typefinding
pipeline의 normal part임 (부분임)
GStreamer는 typefinding을 통해 type을 알아냄 (보통)
typefind는
data를 읽어 들이면서 type을 찾음 (찾을때까지 읽음)
이 때 모든 plugin에 data를 제공함
typefinding(typefind elem)은 typefinder를 구현하는 모든 plugin들에 data를 제공
¡ typefind elem
signal을 emit하고
여기서 passthrough module로 동작함
type이 발견되지 않으면,
error를 emit하고 media processing을 stop
elem이 type을 typefind elem이 찾으면,
app이 이것을 가지고 pipeline에 plug할때 사용
¡ typefinder 기능
이 기능을 구현한 elem은 media type을 제공하게 되어 있음
- data를 받고 살펴본 후 media type을 확인
- 모든 elem에 대해 처리하고 나면 app은 모든 type을 알게 됨
그런데,
보통 file extension으로 파악하기도 함
ex. detected media type
static void
cb_typefound (GstElement *typefind,
guint probability,
GstCaps *caps,
gpointer data)
{
GMainLoop *loop = data;
gchar *type;
type = gst_caps_to_string (caps);
g_print ("Media type %s found, probability %d%%\n", type, probability);
g_free (type);
/* since we connect to a signal in the pipeline thread context, we need
* to set an idle handler to exit the main loop in the mainloop context.
* Normally, your app should not need to worry about such things. */
g_idle_add (idle_exit_loop, loop);
}
...
main (...
{
loop = g_main_loop_new (NULL, FALSE);
pipeline = gst_pipeline_new ("pipe");
bus = gst_pipeline_get_bus (GST_PIPELINE (pipeline));
gst_bus_add_watch (bus, my_bus_callback, NULL);
gst_object_unref (bus);
filesrc = gst_element_factory_make ("filesrc", "source");
g_object_set (G_OBJECT (filesrc), "location", argv[1], NULL);
typefind = gst_element_factory_make ("typefind", "typefinder");
g_signal_connect (typefind, "have-type", G_CALLBACK (cb_typefound), loop);
...
fakesink = gst_element_factory_make ("fakesink", "sink");
/* setup */
gst_bin_add_many (GST_BIN (pipeline), filesrc, typefind, fakesink, NULL);
gst_element_link_many (filesrc, typefind, fakesink, NULL);
gst_element_set_state (GST_ELEMENT (pipeline), GST_STATE_PLAYING);
g_main_loop_run (loop);
/* unset */
gst_element_set_state (GST_ELEMENT (pipeline), GST_STATE_NULL);
gst_object_unref (GST_OBJECT (pipeline));
어느 시점에 callback이 호출되는지 파악 (돌려보면서) 필요
plug 시점
일단, media type이 파악 된 후에야 elem을 plug 할 수 있음
15.2. Dynamically autoplugging a pipeline
see CH. 20
16. Pipeline manipulation
app에서 pipeilne으로 data 추가 방법
pipeline에서 data read 방법
pipeline의 속도, length, starting point 제어 방법
pipeline의 data processing을 listen 하는 방법
16.1. Using probes
¡ probe는 pad listenner임 (즉, callbabck)
pad에 attach 됨 (gst_pad_add_probe)
pad에서 제거는
gst_pad_remove_probe()
¡ probe
pad 상의 activity를 notify 함
u - buffers,
u - events
u - queries
pad에 어떤 것을 listen 할지 정의 가능
pad가 probe로 notify 하는 activities
¡ 1) buffer PULL/PUSH
buffer가 pushed 혹은 pulled인 경우, probe에 등록하려면,
GST_PAD_PROBE_TYPE_BUFFER
다음의 flag로 어떤 mode에 대해 관심 있는지 표시 가능
GST_PAD_PROBE_TYPE_PUSH
GST_PAD_PROBE_TYPE_PULL
probe로
버퍼에 대해 inspect, modify, drop 가능
¡ 2) bufferlist가 pushed
GST_PAD_PROBE_TYPE_BUFFER_LIST
bufferlist가 push 되면, probe에 등록할 때 이것으로 등록
event는
pad를 거쳐 travel함
¡ 3) pad를 통한 event 받기
받을 event의 방향 설정
GST_PAD_PROBE_TYPE_EVENT_DOWNSTREAM
or
GST_PAD_PROBE_TYPE_EVENT_UPSTREAM
or
GST_PAD_PROBE_TYPE_EVENT_BOTH 가능
flush event
기본적으로는 notification을 만들지 않음
받으려면,
GST_PAD_PROBE_TYPE_EVENT_FLUSH 을 명시적으로 enable 해야 함
(push mode에서만 noti 함)
이 probe로 event를 inspect, modify or drop 가능
¡ 4) pad를 통한 query 받기
GST_PAD_PROBE_TYPE_QUERY_DOWNSTREAM
GST_PAD_PROBE_TYPE_QUERY_UPSTREAM
로 downstream/upstream 선택
GST_PAD_PROBE_TYPE_QUERY_BOTH
둘 다 선택
query probe는 2회 noti 됨
- 한번은 up/down 시,
- 다른 한번은 query result가 return 될 때
GST_PAD_PROBE_TYPE_PUSH
GST_PAD_PROBE_TYPE_PULL
각각 query 수행 시,
query가 result를 return 시에 callback이 발생함을 의미
이 probe로 query에 대해 inspect, modify 가능
probe callback에서 query에 대한 answering을 할 수 있음
- query 내 result value를 위치시킴으로서
- 그리고 GST_PAD_PROBE_DROP을 callback에서 reutrn
¡ 5) dataflow에 대한 noti
probe에 dataflow를 block 요청 가능
callback이 return 시
사용 경우
- unlinked 경우
- unlink 하려는 경우
이런 경우 unblock이 아니면,
unlinked pad에 data pushed 시 pipeline은 error state로 천이됨
blocking probe라고 불림
GST_PAD_PROBE_TYPE_BLOCK flag로 활성화 됨
이를 설정하면 선택된 activity 상의 dataflow를 block 할수 있음
probe 제거 시 pad는 다시 unblock됨
(callback에서 GST_PAD_PROBE_REMOVE 리턴 시)
현재 block 된 item을 pass 시키려면,
GST_PAD_PROBE_PASS을 callback에서 return (다음에는 다시 block됨)
¡ 6) idle probe
no activity에 대한 noti
GST_PAD_PROBE_TYPE_IDLE flag로 probe 설정 시,
GST_PAD_PROBE_TYPE_PUSH / GST_PAD_PROBE_TYPE_PULL
를 명시하여 해당 경우에 대해서만 noti 받을 수도 있음
idle probe는 blocking probe이기도 함
- idle probe가 설치 된 이상 pad 상으로 data를 pass 시키지 않기 때문
idle probe들이 동적으로 pad를 relink할 수 있도록 가능함
16.1.1. Data probes
¡ pad 상에 data가 지나갈때 noti.
이 probe를 더하려면,
GST_PAD_PROBE_TYPE_BUFFER and/or GST_PAD_PROBE_TYPE_BUFFER_LIST
를 명시
¡ data probe 동작
pipeline streaming thread context에서 동작
(Data probes run in pipeline streaming thread context)
callback은 not block이고 보통 이상한 stuff을 수행하지 않음
여기서 뭔가하면 pipeline 성능에 부정적 영향을 미침
bug가 있는 경우 crash나 deadlock 야기
이 probe callback에서 GUI 관련 동작도 하면 안되고,
pipeline의 state chagne도 하면 안됨
app은 custom message를 pipeline의 bus에 post하고,
이런 것이 pipeline을 stop 시킬 수도 있음
¡ _chain()
대부분의 elem 상의 common buffer 동작은 _chain에서 수행됨
이것이 probe callback에서도 수행될 수 있음
ex. p89
static GstPadProbeReturn
cb_have_data (GstPad *pad,
GstPadProbeInfo *info,
gpointer user_data)
...
{
buffer = GST_PAD_PROBE_INFO_BUFFER (info);
buffer = gst_buffer_make_writable (buffer);
gst_buffer_map (buffer, &map, GST_MAP_WRITE);
ptr = (guint16 *) map.data;
/* invert data */
for
for
ptr[..] 조작
gst_buffer_unmap (buffer, &map);
GST_PAD_PROBE_INFO_DATA (info) = buffer;
return GST_PAD_PROBE_OK;
}
main
...
pipeline = gst_pipeline_new ("my-pipeline");
src = gst_element_factory_make ("videotestsrc", "src");
filter = gst_element_factory_make ("capsfilter", "filter");
csp = gst_element_factory_make ("videoconvert", "csp");
sink = gst_element_factory_make ("xvimagesink", "sink");
gst_bin_add_many (GST_BIN (pipeline), src, filter, csp, sink, NULL);
gst_element_link_many (src, filter, csp, sink, NULL);
GstCaps *filtercaps = gst_caps_new_simple ("video/x-raw",
"format", G_TYPE_STRING, "RGB16",
"width", G_TYPE_INT, 384, "height", G_TYPE_INT, 288,
"framerate", GST_TYPE_FRACTION, 25, 1, NULL);
g_object_set (G_OBJECT (filter), "caps", filtercaps, NULL);
gst_caps_unref (filtercaps);
pad = gst_element_get_static_pad (src, "src");
gst_pad_add_probe (pad, GST_PAD_PROBE_TYPE_BUFFER,
(GstPadProbeCallback) cb_have_data, NULL, NULL);
gst_object_unref (pad);
gst_element_set_state (pipeline, GST_STATE_PLAYING);
/* wait until it’s up and running or failed */
if (gst_element_get_state (pipeline, NULL, NULL, -1) == GST_STATE_CHANGE_FAILURE)
...
...
Compare that output with the output of “gst-launch-1.0 videotestsrc ! xvimagesink
¡ pad probe callback
버퍼가 writable인 경우에만 buffer의 수정이 가능함
gst_buffer_is_writable로 check 해서 가능 시에만 수정해야 bug를 야기하지 않음
pad probe는
- data를 조사하는데 가장 적합함
data의 수정이 필요한 경우
- pad probe에서 하는것은 보통 바람직하지 않음
- elem.을 새로 만들어서 수행하는 것이 바람직함
GstAudioFilter, GstVideoFilter, GstBaseTransform 등을 사용하면 수비게 가능
¡ Identity element
검사만 하고자 하는 경우에도...
identity elem.을 pipeline에 추가하고,
identity elem의 "handoff" signal에 연결
debugging 용도
"dump" property
"last-message" property
(gst-launch에 -v 주던가 혹은 silent property에 FALSE 주면 활성화)
16.1.2. Play a region of a media file
¡ 2초에서 5초 구간만 재생하고 EOS 처리 하는 방식
¡ 방식
1) uridecodebin element을 PAUSED state로 천이 (모든 source pad를 block)
2) 모든 source pad에 data가 있음 (prerolled)
3) prerolled pipeline에 대해
media의 duration을 요청한 후 seek 할 수 있음
4) 관심 region을 설정한 후, sink elem을 연결하고,
source pad를 unblock하여 pipeline이 PLAYING state로 가게 함
5) sink에 의해 재생 중임을 알 수 있음 (EOS 전까지)
ex.
static GMainLoop *loop;
static volatile gint counter;
static GstBus *bus;
static gboolean prerolled = FALSE;
static GstPad *sinkpad;
dec_counter (GstElement * pipeline) {
if (prerolled)
return
if (g_atomic_int_dec_and_test (&counter))
prerolled = TRUE;
gst_bus_post (bus, gst_message_new_application(
GST_OBJECT_CAST (pipeline),
gst_structure_new_empty ("ExPrerolled")));
}
cb_blocked (GstPad *pad,
... {
GstElement *pipeline = GST_ELEMENT (user_data);
if (prerolled)
return GST_PAD_PROBE_REMOVE;
dec_counter (pipeline);
return GST_PAD_PROBE_OK;
}
cb_pad_added (GstElement *element,
... {
GstElement *pipeline = GST_ELEMENT (user_data);
if (prerolled)
return
g_atomic_int_inc (&counter);
gst_pad_add_probe (pad, GST_PAD_PROBE_TYPE_BLOCK_DOWNSTREAM,
(GstPadProbeCallback) cb_blocked, pipeline, NULL);
gst_pad_link (pad, sinkpad);
}
cb_no_more_pads (GstElement *element,
... {
GstElement *pipeline = GST_ELEMENT (user_data);
if (prerolled)
return
dec_counter (pipeline);
}
cb_message (GstBus *bus,
GstMessage *message,
...
{
GstElement *pipeline = GST_ELEMENT (user_data);
switch (GST_MESSAGE_TYPE (message)) {
case GST_MESSAGE_ERROR:
g_main_loop_quit (loop);
case GST_MESSAGE_EOS:
g_main_loop_quit (loop);
case GST_MESSAGE_APPLICATION:
if (gst_message_has_name (message, "ExPrerolled"))
g_print ("we are all prerolled, do seek\n");
gst_element_seek (pipeline,
1.0, GST_FORMAT_TIME,
GST_SEEK_FLAG_FLUSH | GST_SEEK_FLAG_ACCURATE,
GST_SEEK_TYPE_SET, 2 * GST_SECOND,
GST_SEEK_TYPE_SET, 5 * GST_SECOND);
gst_element_set_state (pipeline, GST_STATE_PLAYING);
...
main (gint argc,
...
{
GstElement *pipeline, *src, *csp, *vs, *sink;
....
pipeline = gst_pipeline_new ("my-pipeline");
bus = gst_pipeline_get_bus (GST_PIPELINE (pipeline));
gst_bus_add_signal_watch (bus);
g_signal_connect (bus, "message", (GCallback) cb_message, pipeline);
src = gst_element_factory_make ("uridecodebin", "src");
g_object_set (src, "uri", argv[1], NULL);
csp = gst_element_factory_make ("videoconvert", "csp");
vs = gst_element_factory_make ("videoscale", "vs");
sink = gst_element_factory_make ("autovideosink", "sink");
gst_bin_add_many (GST_BIN (pipeline), src, csp, vs, sink, NULL);
gst_element_link_many (csp, vs, sink, NULL);
sinkpad = gst_element_get_static_pad (csp, "sink");
g_atomic_int_set (&counter, 1);
g_signal_connect (src, "pad-added",
(GCallback) cb_pad_added, pipeline);
g_signal_connect (src, "no-more-pads",
(GCallback) cb_no_more_pads, pipeline);
gst_element_set_state (pipeline, GST_STATE_PAUSED);
g_main_loop_run (loop);
gst_element_set_state (pipeline, GST_STATE_NULL);
gst_object_unref (sinkpad);
gst_object_unref (bus);
gst_object_unref (pipeline);
g_main_loop_unref (loop);
...
}
¡ custom message
uridecidebin이 preroll 되어 있는 main thread에 custom message를 사용할 수 있음
main thread가 이걸 받은 후 requested region으로 flushing seek을 요청 (issue)
seek은 일시적으로 pad를 unblock하고, 새로운 data가 오면 reblock
probe를 제거하기 위해 이 두 번째 block을 감지하고,
pipeline을 PLAYING state로 set 하면,
2에서 5초를 재생 후 EOS를 발생
16.2. Manually adding or removing data from/to a pipeline
¡ pipeline에 특정 data를 넣기 혹은 pipeline의 data 받기
언제나 plugin을 새로 만들고 base class들을 사용하는 것이 좋음
Plugin Writer's Guide를 보면 됨
이런 경우에 사용 가능한 elem들
1) appsrc (imaginary source)
2) appsink (imaginary sink)
이런 elem들에 동일한 방식이 적용됨
16.2.1. Inserting data with appsrc
¡ appsrc 사용
설정 필요
동작 mode: push/pull
"random-access"가
¡ preroll
camera가 roll된 후 action 되기 전까지의 기간
¡ appsrc 예제
. data를 pipeline에 insert하는 예제
. 몇 가지 설정이 있음
¡ 설정
. push / pull mode 설정
- stream-type property를 사용해서 제어
- stream-type이 "random-access"인 경우 pull mode
else 면, push mode
¡ . buffer의 caps 설정
- caps property로 설정
¡ . live mode
- is-live property 설정으로 live mode로 설정 가능
- live mode는 min-latency와 max-latency 설정이 중요함
min-latency: buffer capture와 appsrc로 pushed 되는 시간 이어야 함
max-latency
live mode에서는 pipeline running-time을 가지고 buffer에 timestamp를 줘야 함
이 시간은 buffer의 first byte가 획득 되는 시간
¡ . do-timestamp property
- 이 perperty로 appsrc가 timestamp 할 수 있음
- min-latency는 0가 되어야 함
buffer가 appsrc로 들어가는 running-time을 기준이기 timestamping 하기 때문
¡ . SEGMENT event format
buffer의 running-time을 어떻게 계산할지를 암시함
반드시 이해하고 설정해야 함
live source에 대해 GST_FORMAT_TIME에 format property를 설정
non-live source의 경우 media type에 의존
buffer에 timestamp를 주고자 하는 경우,
GST_FORMAT_TIME format을 넣어야 함 그렇지 않은 경우 GST_FORMAT_BYTES가 적절함
¡ . random-access mode
- appsrc의 size property에 stream 내 byte의 수를 설정해야 함
- downstream elemtn들이 media의 size를 알 수 있게 하고 필요시 EOS로 갈 수 있게 함
¡ appsrc에 data를 handling하는 방법
gst_app_src_push_buffer()
or
push-buffer action signal 을 emit
이로서 buffer를 appsrc의 queue에 넣을 수 있음
(appsrc 내 streaming thread가 consume)
push-buffer call을 수행하는 thread로부터의 data transport는 발생하지 않음
¡ max-bytes property
queue에 얼마나 많은 data를 넣을지 제어하는 property
queue가 차면 "enough-data" signal을 발생
받으면 app은 data의 push를 멈춰야함
¡ "block" property
appsrc가 push-buffer method를 data의 처리 가능시 까지 block 함
¡ need-data signal
내부 queue에 data가 running out되면 발생
app은 이 signal을 받으면 data를 feeding하면 됨
¡ seek-data signal
stream-mode property가 "seekable" 혹은 "random-access"로 설정 되어 있는 경우,
appsrc는 "seek-data" signal을 emit 할 수 있음
이 signal argument는 stream 내 원하는 position을 포함
("format" property을 가지고 unit set에 표현됨)
app이 이 seek-data signal을 받으면,
app은 새로운 position으로부터 push-buffer 해야 함
¡ EOS
마지막 byte를 appsrc에 push한 이후,
gst_app_src_end_of_stream()을 호출하여 appsrc가 EOS downstream을 보내게 해야함
이러한 signal들로, app이 appsrc를 push 혹은 pull mode로 동작할 수 있게 함
16.2.1.1. Using appsrc in push mode
¡ appsrc - push mode
stream-type = "seekable" <- seek-data callback 구현 필요
이 model로 여러 network protocol을 구현하는데 사용됨
app은 반복적으로 새로운 buffer를 가지고 push-buffer method를 호출
옵션으로, appsrc의 queue size는 enough-data와 need-data signal을 통해 제어 가능
min-percent property
내부 appsrc queue가 어떻게 empty 가 발생할지 제어 (보통 0 이상으로 설정해 completely draining을 피함)
16.2.1.2. Using appsrc in pull mode
¡ appsrc - pull mode
appsrc가 need-data signal handler를 호출하면,
여기서 need-data signal에서 요청된 data 크기 만큼을 채우면 됨
EOS의 경우에만 이보다 적은 data를 push 하는 것이 허용됨
file access 혹은 other randomly accessible source에 이 model을 사용
Xv-window output에 black/white video를 생성
colorspace conversion element를 사용
variable framerate (0/1)
outgoing buffer에 timestamp 설정
초당 2개 frame
¡ pull mode method of pushing new buffers
p96 example
static GMainLoop *loop;
static void
cb_need_data (GstElement *appsrc,
guint unused_size,
gpointer user_data) {
...
buffer = gst_buffer_new_allocate (NULL, size, NULL);
gst_buffer_memset (buffer, 0, white ? 0xff : 0x0, size);
GST_BUFFER_PTS (buffer) = timestamp;
GST_BUFFER_DURATION (buffer) = gst_util_uint64_scale_int (1, GST_SECOND, 2);
timestamp += GST_BUFFER_DURATION (buffer);
g_signal_emit_by_name (appsrc, "push-buffer", buffer, &ret);
gst_buffer_unref (buffer);
...
}
gint
main(...) {
appsrc = gst_element_factory_make ("appsrc", "source");
g_object_set (G_OBJECT (appsrc), "caps",
gst_caps_new_simple ("video/x-raw",
"format", G_TYPE_STRING, "RGB16",
"width", G_TYPE_INT, 384,
"height", G_TYPE_INT, 288,
"framerate", GST_TYPE_FRACTION, 0, 1, NULL), NULL);
gst_bin_add_many (GST_BIN (pipeline), appsrc, conv, videosink, NULL);
gst_element_link_many (appsrc, conv, videosink, NULL);
g_object_set (G_OBJECT (appsrc), "stream-type", 0, "format", GST_FORMAT_TIME, NULL);
g_signal_connect (appsrc, "need-data", G_CALLBACK (cb_need_data), NULL);
gst_element_set_state (pipeline, GST_STATE_PLAYING);
g_main_loop_run (loop);
...
}
16.2.2. Grabbing data with appsink
¡ appsink
. pull/push model 지원
. gst_app_sink_pull_sample()
gst_app_sink_pull_preroll()
로 data 획득
"pull-sample"
"pull-preroll" signals
blocking method임
- data의 획득 시 까지 혹은 EOS 까지 block 됨
내부에서 queue 사용
- "max-buffers" property로 queue size 설정
- "drop" property로 older buffer의 drop 가능 (queue size max 도달 시)
- blocking은 real-time 성능에 부정적 영향을 미치기에 피해야 함
¡ "emit-signals" property
blocking 사용 안하는 경우, TRUE 설정
"new-sample", "new-preroll" signal을 발생함 (sample을 pull 해야 하는 경우)
¡ "caps" property
appsink가 받는 format 설정
non-fixed caps 임
sample caps를 받아서 pulled sample의 format을 알 수 있음
¡ pull-preroll / pull-sample methods
NULL return 경우,
appsink는 stop 되던가 혹은 EOS 상태로 진입
gst_app_sink_is_eos() 혹은 "eos" property로 EOS state check 가능
¡ 설정 필요 properties
. "sync" property
sink base class가 sample 처리 전에 pupieline clock에 반하여
buffer에 대해 동기화 하게 만들고자 하는 경우,
. "qos" property
Quality-of-Service
raw video frame 처리 시에 base class가 clock에 동기화 되게 하고자 하는 경우,
base class가 QOS event를 upstream으로 보내게 하는 것
. cap property
upstream elememnt들은 format conversion을 시도하여
appsink의 cap에 맞도록 할 것임
GstSample을 check 해서 buffer에 대한 실제 caps을 얻어야 함
appsink를 사용해 video snapshot을 capture하는 방법
ex. 100p
16.3. Forcing a format
video size, format,
audio bitsize, number of channels 등 설정 하고자 하는 경우,
pipeline의 GstCaps를 강제하여 설정 가능
¡ filtered caps
를 통해 가능
link 상의 filtered caps는 두 elem 사이의 "capsfilter" element를 사용해 설정
이 "capsfilter" element의 "caps" property를 GstCaps로서 설정
16.3.1. Changing format in a PLAYING pipeline
PLAYING state에서 pupeline의 format을 동적으로 변경 가능
capsfilter의 caps property만 바꿔주면 가능함
capsfilter는 RECONFIGURE event를 upstream으로 보놰면,
upstream element들이 새로운 format과 allocator에 대해 renegotiation 수행
(upstream elememt들이 source pad 상에서 fixed caps를 사용하지 않아야 동작함)
ex. p 102
pipe = gst_parse_launch_full ("videotestsrc ! capsfilter name=filter ! "
"ximagesink", NULL, GST_PARSE_FLAG_NONE, NULL);
filter = gst_bin_get_by_name (GST_BIN (pipe), "filter");
gst_element_set_state (pipe, GST_STATE_PLAYING);
// 될 때 까지 아래 caps의 width/height 값을 변경 해 가면서 설정 변경
capsstr = g_strdup_printf ("video/x-raw, width=(int)%d, height=(int)%d", width, height);
caps = gst_caps_from_string (capsstr);
g_object_set (filter, "caps", caps, NULL);
message = gst_bus_poll (GST_ELEMENT_BUS (pipe), GST_MESSAGE_ERROR, 50 * GST_MSECOND);
gst_bus_poll()을 사용해서 message를 받을 경우, 출력 필요 (null이 아닌 경우)
;를 delimeter로 하여 여러 caps를 capsfilter에 설정 가능
capsfilter는 최초 것 부터 negotiation 수행
16.4. Dynamically changing the pipeline
¡ pipeline의 동적 수정(modification)
PLAYING state에서 flow를 끊지 않고 pipeline을 변경
¡ building dynamic pipelines
. removing elements
unlinked pad에 data flow가 없어야 함 (에러 유발)
늘 push mode 시 source pad를 block, 혹은 pull mode 시 sink pad를 block하고 pad를 unlink
. adding elements
element의 state를 parent와 동일 state로 set 하고 dataflow
(그냥 data flow시 최초 NULL state이기에 error)
기본 clock 사용 & pipeline의 현재 base-time 사용
이로서 새 elem은 기존 elem과 동일 running-time을 설정 가능
sink는 buffer를 다른 sink처럼 동기화 가능하고 source는 다른 source에 match 되는
running-time에 buffer를 생성
. unlinking elements
upstream chain에서 제거 시,
EOS event를 down으로 보내 (elememtn sink pad) flush 상태가 되도록 해야 함
이렇게 해야만 data의 손실이 없음
... skip
16.4.1. Changing elements in a pipeline
- ----. .-----------. .---- -
element1 | | element2 | | element3
src -> sink src -> sink
- ----’ ’----------’ ’---- -
¡ PLAYING state에서 elem2를 elem4로 바꾸고자 함
1) block elem1's source pad with a blokcing pad probe to stop dataflow
probe callback will be called after the pad is blocked
2) unlink elem1 and 2
3) flushed out of elem2
by pusing EOS into elem2
put an event probe on elem2's source pad
send EOS to elem2's sinkpad
wait EOS event to appear on elem2's source pad
4) unlinke elem2 and elem3
remove elem2 from the pipeline and set the state to NULLL
5) add elem4 to the pipeline
link elem4 and 3
linke elem1 and 4
6) make sure the elem4's state in the same state as the rest of the elems
should be at leat in the PAUSED state
7) unblock elem1's source pad probe -> continue streaming
ex. p106
adding videoconvert element before and after the effect
(to adjust different colorspaces)
17. IV. Higher-level interfaces for GStreamer applications
standard playback interface
. autopluggers
. playback managing elements
. etc.
18. Chapter 20. Playback Components
. hide the complexity of media type detection and several other rather complex topics
. recommended
plybin or decodebin
¡ playbin
simple playback of media
¡ decodebin
more flexible autoplugger
could add more advanced features such as playlist, crossfading of audio tracks and so on.
18.1. Playbin
GstElement *play = gst_element_factory_make ("playbin", "play");
g_object_set (G_OBJECT (play), "uri", argv[1], NULL);
bus = gst_pipeline_get_bus (GST_PIPELINE (play));
gst_bus_add_watch (bus, my_bus_callback, loop);
gst_element_set_state (play, GST_STATE_PLAYING);
...
18.1.1. playbin의 several features
. settable output ("video-sink" & "audio-sink" properties)
. error, eos, tag, state, media position, seeking
. buffers network-sources
. visualizations for audio-only media
. subtitle
- subtitle from media itself
- subtitle from separate files
: for separate subtitle files, use the "suburi" property
. stream selection / disabling
- from multiple tracks (audio, subtitle), it can choose which one to play back
or decide to turn it off altogether
“gst-launch-1.0 playbin uri=file:///path/to/file”
18.2. Decodebin
Decodebin : actual autoplugger backend of playbin
. accept input from a source that is linked to its sinkpad and will try to detet the media type contained in the stream,
and set up decoder routines for each of those.
-> automatically select decoders
. "pad-added" signal
for each decoded stream, it will emit the signal to let the client know
or "unknown-type" signal
p114 ex.
¡ 가능 사항들
무한의 갯수로 decoded output pad로 decode 가능
tag, error forwarding, state handling 등을 GstElement 식으로 처리 가능
¡ 불가 사항들
알려진 media type들에 대한 input 처리 불가 (DVD, audio-CD 등)
. stream 선택 불가
. decoded video stream 상의 subtitle overlay 불가
gst-launch-1.0 filesrc location=file.ogg ! decodebin ! audioconvert ! audioresample ! autoaudiosink.
18.3. URIDecodebin
¡ decodebin과 유사
주어진 URI를 가지고 source만 auto plugging을 수행함
¡ slow network source
이 경우 buffering element를 자동으로 추가함
buffering element는 BUFFERING message를 post함
(app이 ch. 15에서 설명한 것 수행할 수 있도록 함)
¡ configurations
. buffer-size
. buffer-duration
. download property
. buffering on the parsed/demuxed data with the use-buffering property
p 116
18.4. Playsink
raw decoded audio 및 video, text 에 대한 pad를 요청
¡ features
. GstStreamVolume
. GstVideoOverlay
. GstNavigation
. GstColorBalance
. 자동으로 conversion elem.을 plugging
. no video input 경우, visualization의 rendering을 optionial 처리
. badly muxed file에서 fine-tune 동기화를 위한 A/V sync offset 설정
. last video frame의 snapsnot 기능
ex. p117
audio file에 대해 해당 ex.을 수행하면, visualization 수행함
V. Appendices
how to port GStreamer-0.10 applications to GStreamer-1.0
19. Programs
19.1. gst-launch
gst-launch filesrc location=hello.mp3 ! mad ! audioresample ! osssink
gst-launch filesrc location=redpill.vob ! dvddemux name=demux \
demux.audio_00 ! queue ! a52dec ! audioconvert ! audioresample ! osssink \
demux.video_00 ! queue ! mpeg2dec ! videoconvert ! xvimagesink
¡ gst_parse_launch()
이를 통해 pileline 구성 가능
ex. p121
gst_parse_launch 사용 example
19.1.1. Grammar Reference
gst-launch는 flex/bison parser로 처리됨
'Multimedia > GStreamer' 카테고리의 다른 글
| GStreamer plugin writer's guide: part 1 (0) | 2021.12.22 |
|---|---|
| GStreamer pwg ch. 3 (0) | 2021.12.22 |
| GStreamer pwg ch 4~6 (0) | 2021.12.22 |
| GStreamer pwg ch 7 ~ 9 (0) | 2021.12.22 |
| GStreamer pwg ch 11 (0) | 2021.12.22 |

댓글